Introduction to Arduino Programming
So, let us move on into the programming stage of the SSTuino Innovator’s Kit!
Table of Contents
Virtual Programming
Before we go into programming with the Arduino app, let us take things slow with the coding functionality on TinkerCAD!
The Arduino programming language is very simillar to the C/C++ Language and are actually C/C++ functions that can be called into your code. When the code is uploaded onto the SSTuino, the compiler inside the Arduino IDE will convert it to something that the microcontroller can read.
Create a new circuit on TinkerCAD, and set it up like this:
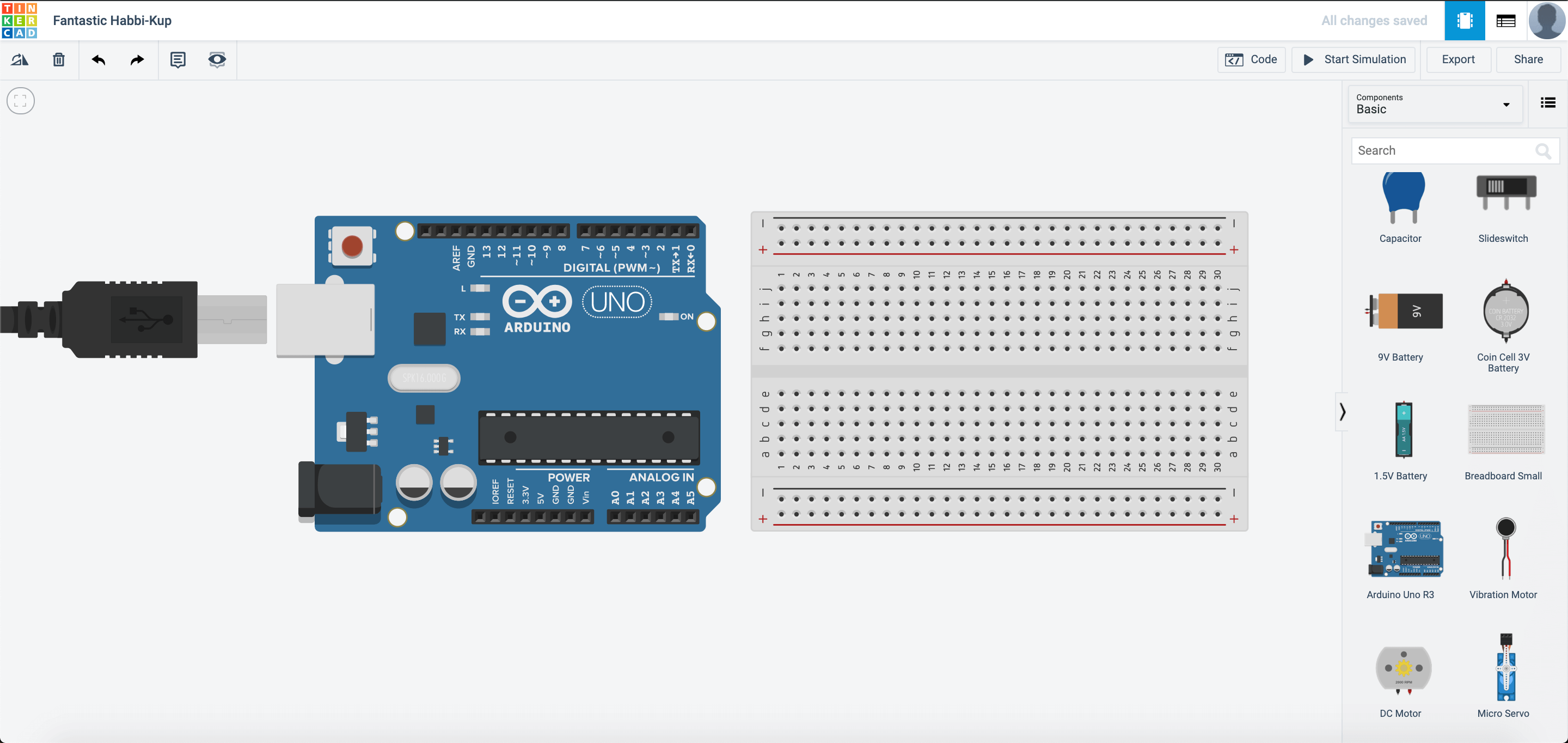
Once you set it up and press start simulation, notice the LED on the Arduino blinking? Why does this happen?
The reason this happens is that TinkerCAD places in a sample code when you insert the Arduino into the circuit.
Stop the simulation and press the CODE button. You should see something like this:
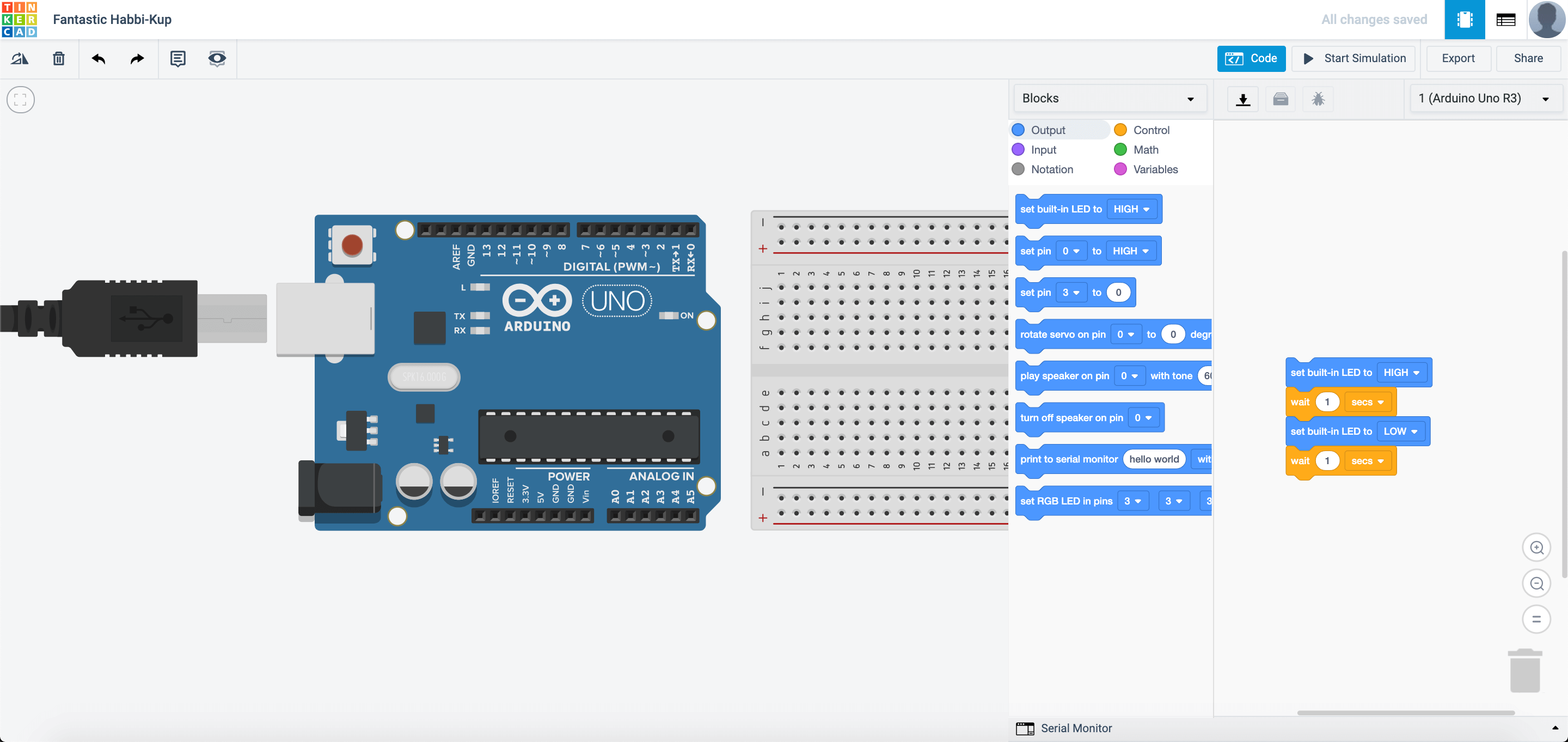
TinkerCAD is very simple to use as you can use block coding to program the Arduino. You would have had experience in block coding with Scratch, Thunkable and Blockly Games. The programming environment would be very simillar to those you had used before.
If you would like to program with text in TinkerCAD, you can also do so like this:
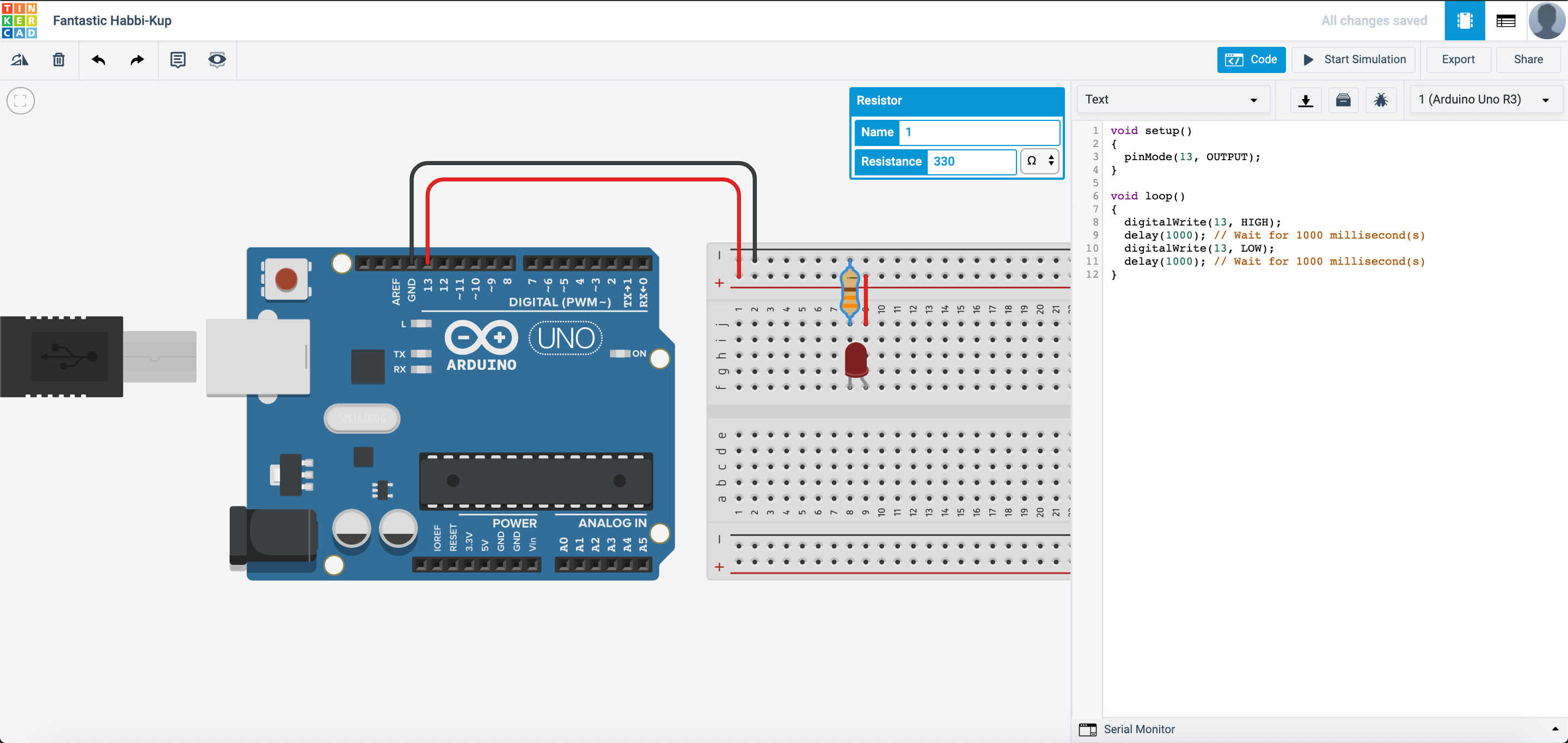
They also have another format called Blocks + Code. The text code changes according to the blocks that you place.
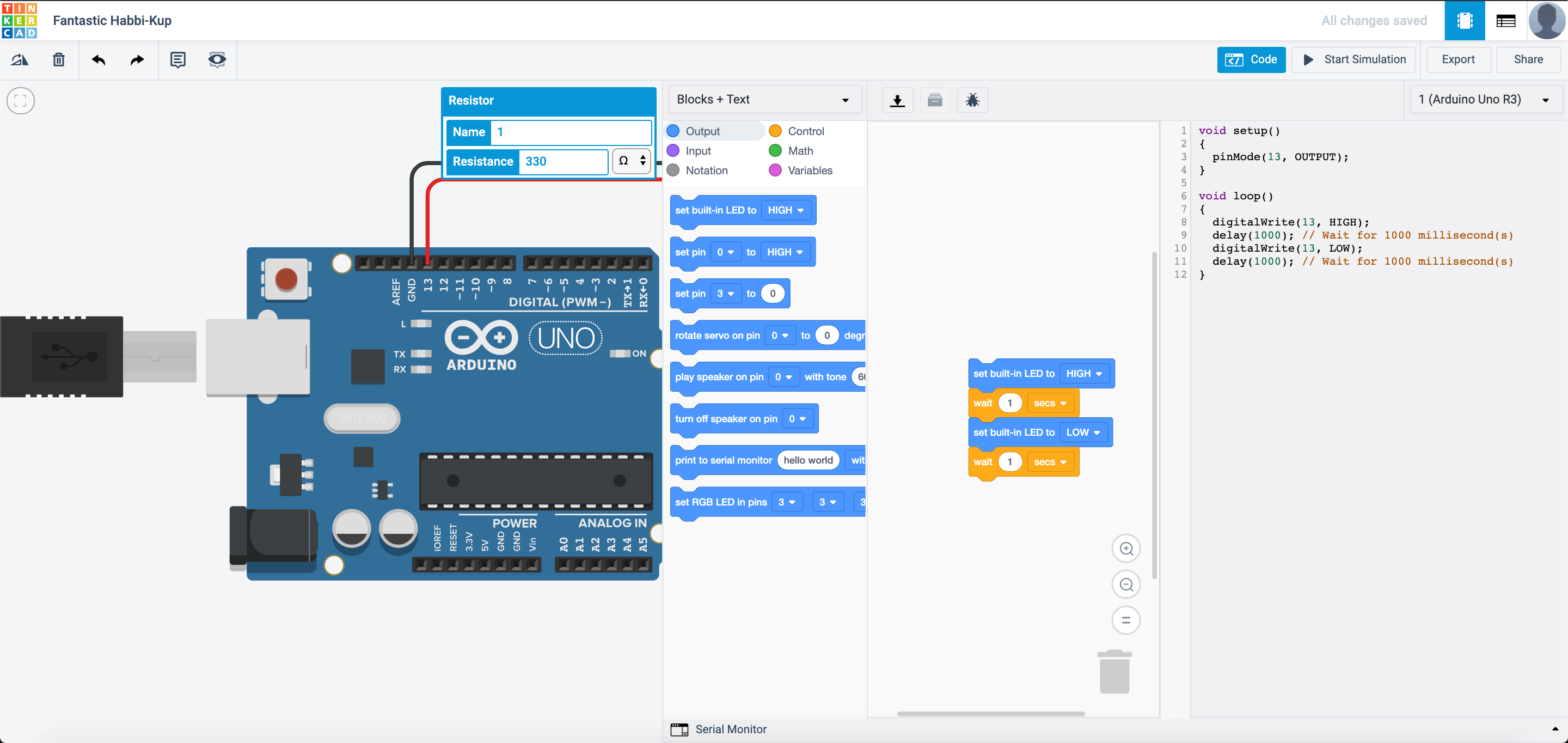
Note: In TinkerCAD, when you program in blocks, the text that you coded will be deleted, and when you program in text, the blocks that you placed will be deleted when you change the programming mode. This is to prevent any internal application error with the website.
So what does this block of code do? It tells the Arduino to:
- Turn on the
built-inLED for one second - Turn off the
built-inLED for one second
and it repeats all over until you turn off the circuit by unplugging the Arduino from the power source.
In programming, HIGH means to turn something on or give it power, while LOW means to turn something off or to not give it power. For this code, there are only 2 STATES, HIGH or LOW. This means that it is either on or off and there is no value in between (either 1 or 0).
Now change the value of the wait ___ seconds to something that you like. What happens then?
Pin 13
Now, let us connect up the circuit:
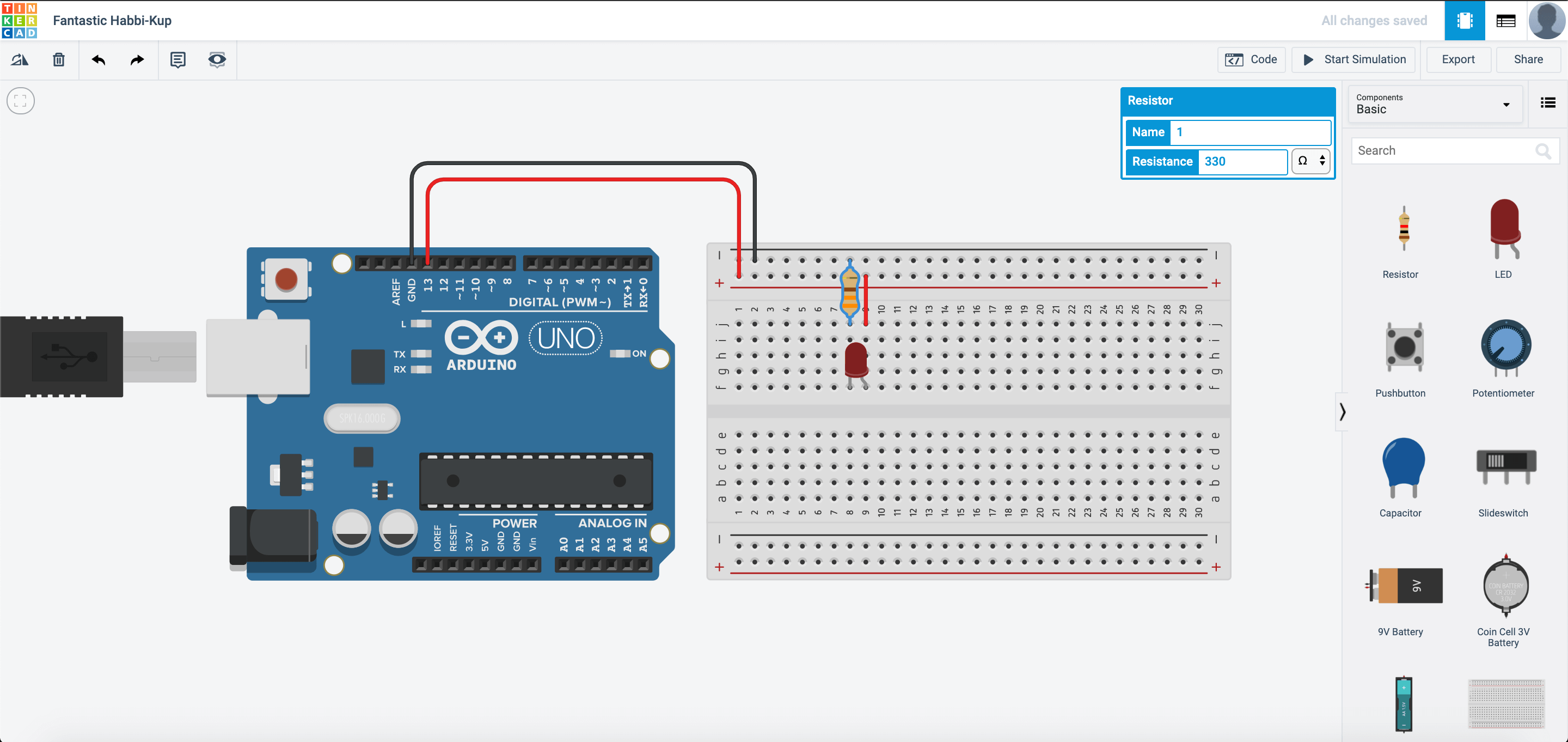
After you start simulation, it should look something like this:
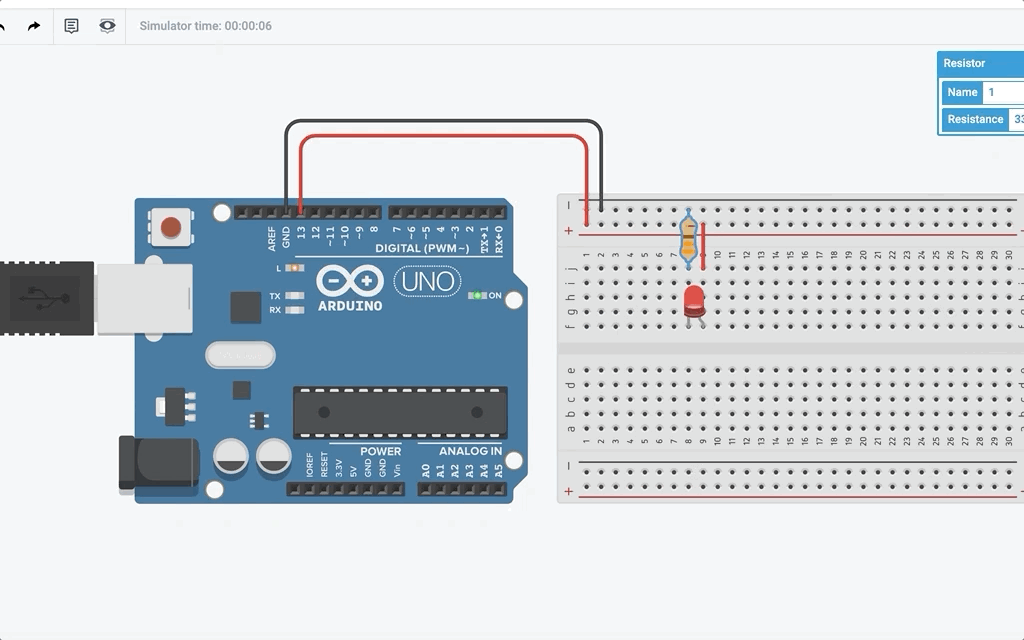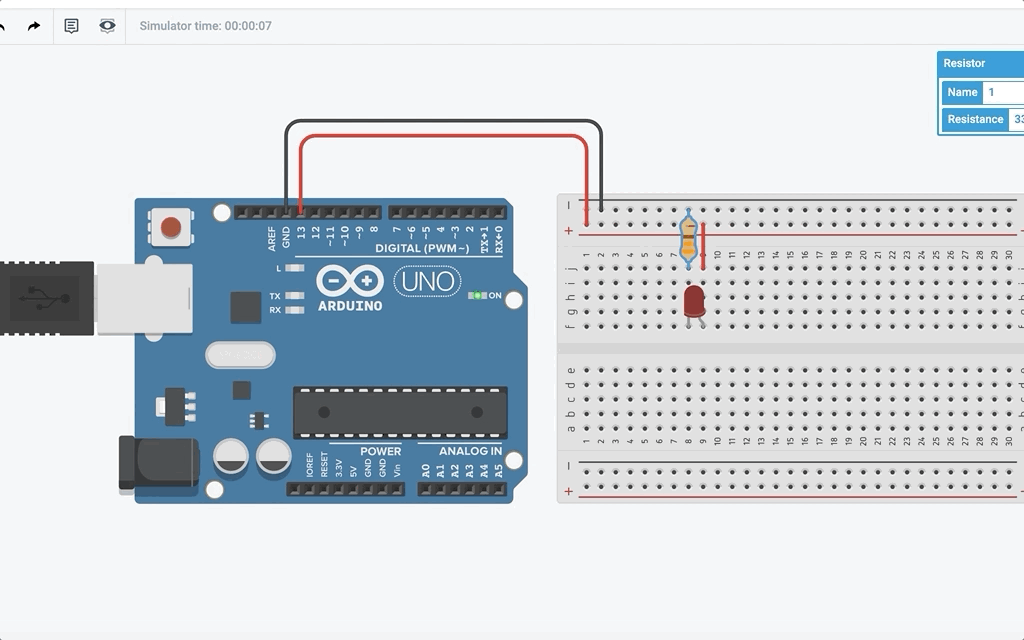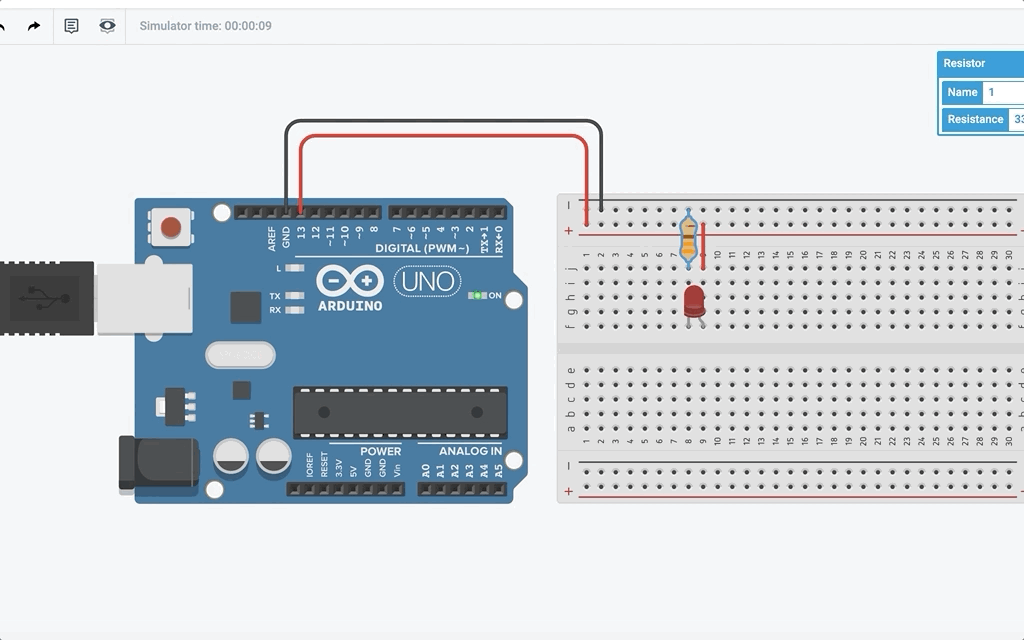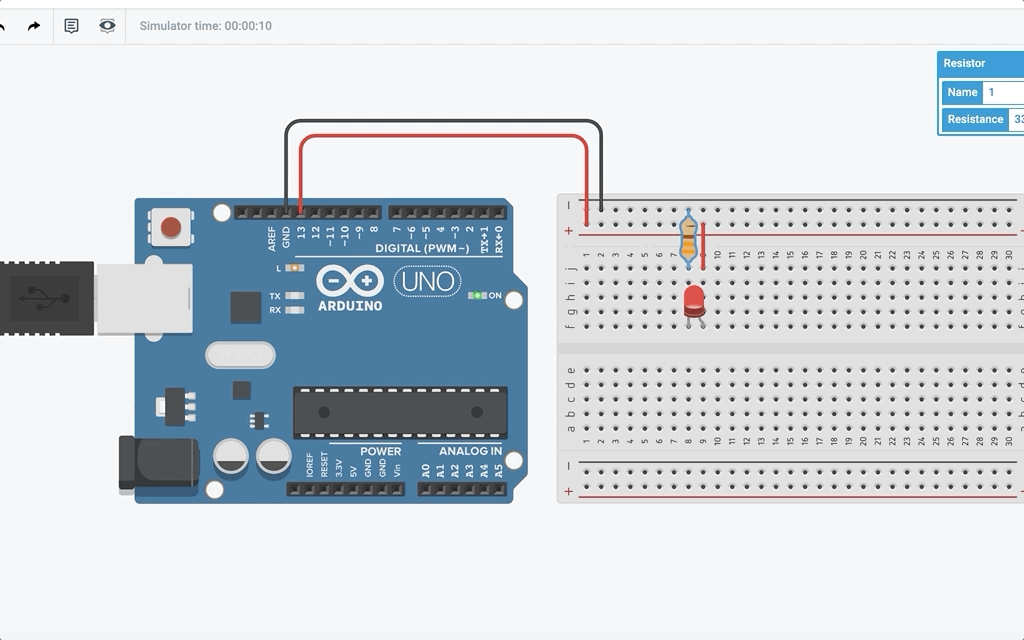
Wait a minute… How come the LED attached turns on and off even though I did not program it? Well the reason behind it is that the built-in LED pin is also connected to pin 13. This means in the program, LED_BUILTIN is also pin 13.
Blink!
In TinkerCAD, another awesome feature is the ability to download the program that you have coded just now! You just have to press the download button as shown here:
Go to code, and press the download button
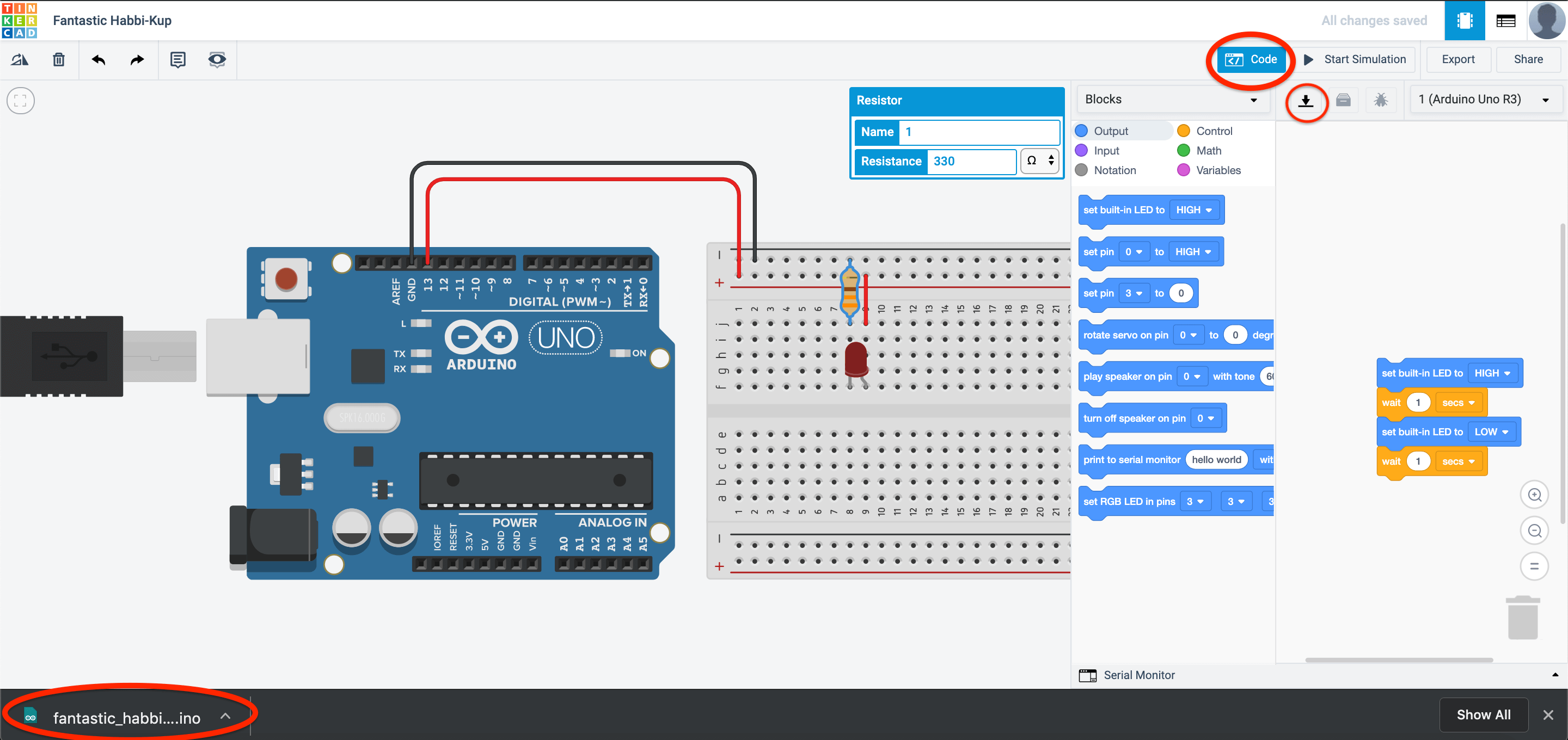
A .ino file will be downloaded on your mac and can be used on the Arduino IDE. Open the file and you would see this:
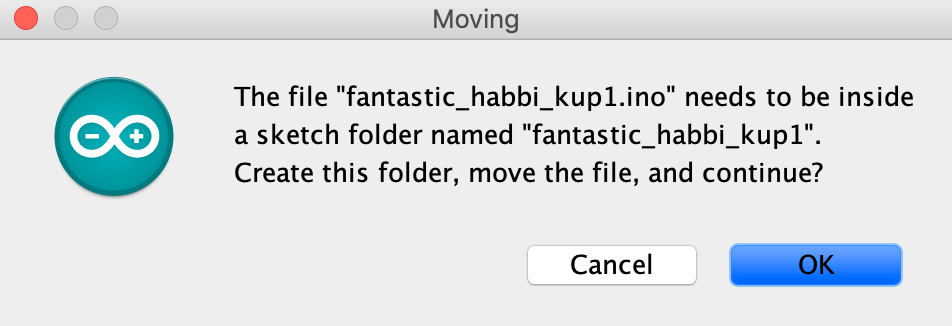
Click OK.
A folder will then be created and you will be able to see this code appear.
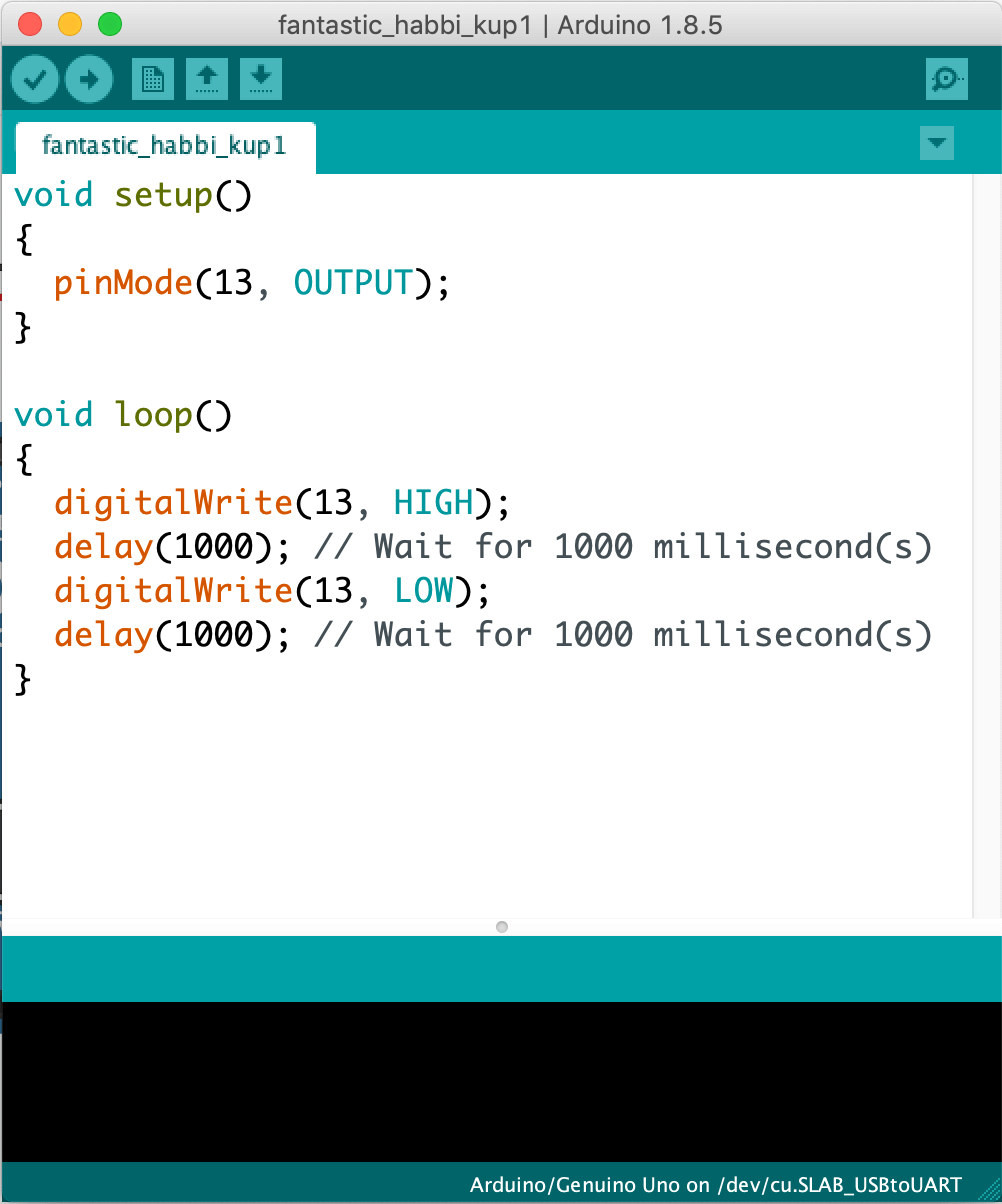
How does the code work?
You would probably have noticed that this code looks rather different than the blocks you see in TinkerCAD. The Arduino app that you are using right now is called an Integrated Development Environment or IDE for short and is one of the places that you can program your SSTuino in.
For example, I use another IDE called Visual Studio Code to modify this website for you! (in Markdown)
Let us analyse the code we see here

Here is an explanation on how most basic Arduino code works:
// These two slashes indicate a comment
/* This also indicates a comment
The brackets () indicate a function e.g. int main()
*/
void setup() //This is only run once when the device first powers up
{ //<- The curly brackets are very important. Place them carefully to avoid confusion.
pinMode(13,OUTPUT);
/*
Why is pinMode written as so? That is due to the practice of using camelCase for writing code.
We declare pin 13 as the output pin. It can also be written as pinMode(LED_BUILTIN, OUTPUT).
The state "OUTPUT" must be written in CAPITAL LETTERS.
It is also very important to place a semicolon ";" when you finish your "sentence", just like
your English sentences.
*/
}
void loop() //loop = runs forever till the end of time (or until you turn off the power)
{
digitalWrite(13, HIGH);// Turn on pin 13
delay(1000); // Wait for 1000 millisecond(s)
digitalWrite(13, LOW);// Turn off pin 13
delay(1000); // Wait for 1000 millisecond(s)
/*
The section above will turn on and off the LED. Note the CAPITAL LETTERS on the "HIGH" and "LOW"
*/
}
Learn more about camelCase here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Camel_case
Learn more about the “()” :http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/functional/function/operator_func/
If you want to read up about C++: http://www.cplusplus.com/
Arduino language reference: https://www.arduino.cc/reference/en/
It WORKS!!!
Now, let us connect our SSTuino like this:
NOTE: To prevent damage to your computer or the components, please disconnect all power from the SSTuino board when you are wiring up your circuit!
Connect the SSTuino to your mac after you have finished assembling the circuit.
In your Arduino IDE, go to
Tools -> Port -> /dev/tty.SLAB_USBtoUART

Make sure to select the correct board:

And now you can upload with this button:
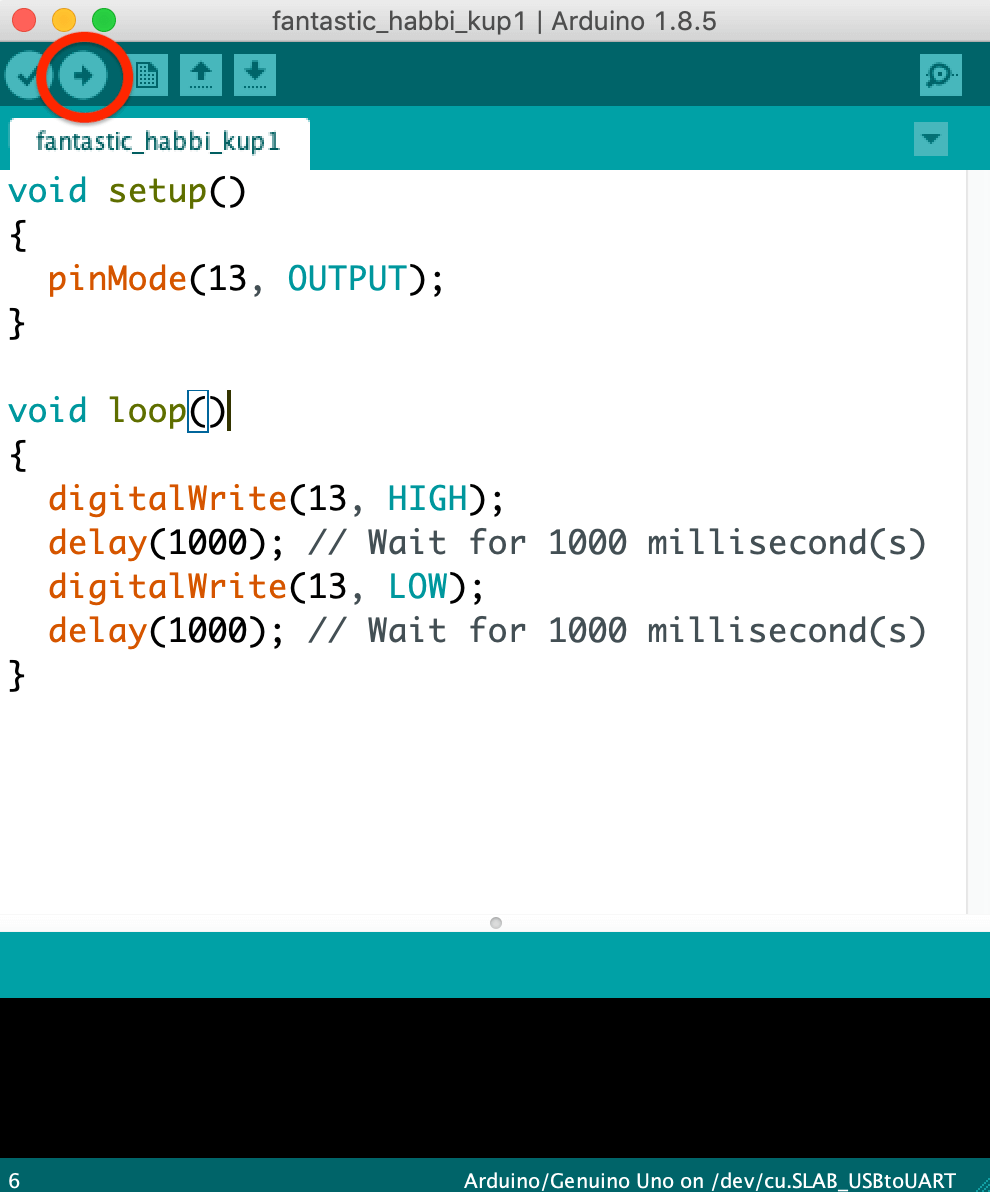
You should see your circuit light up like this:
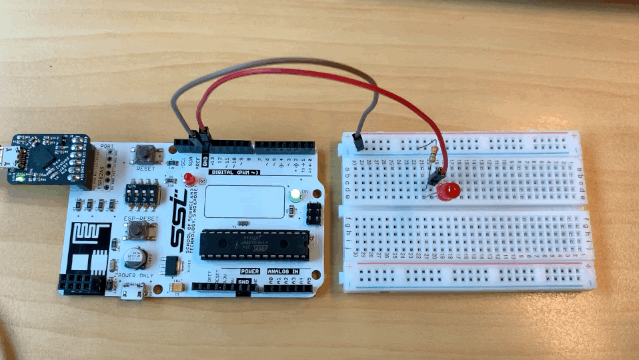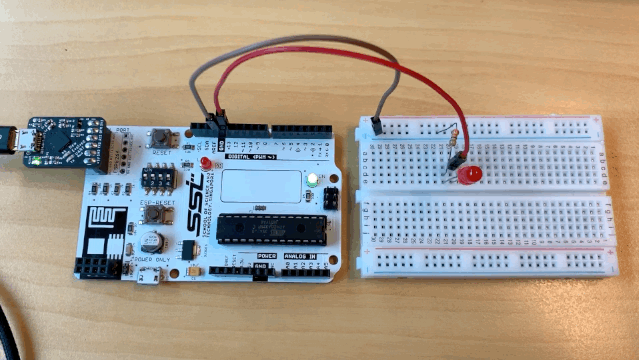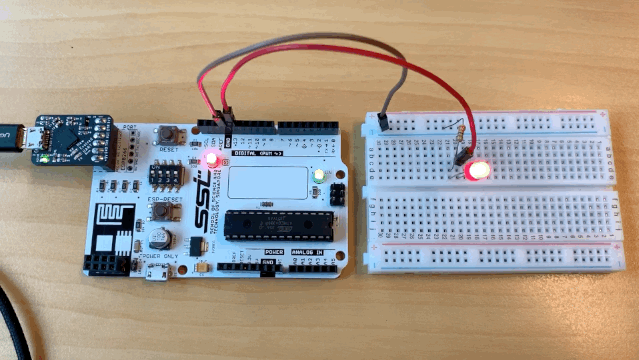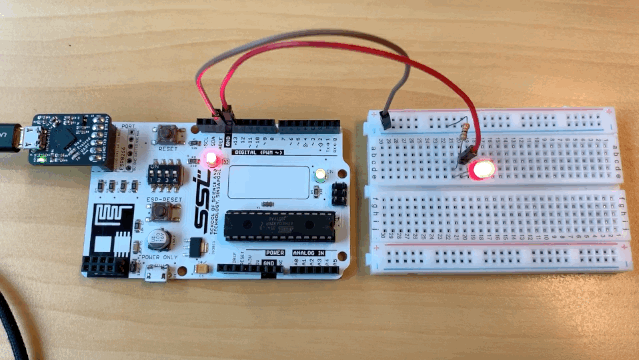
The SSTuino can read?!
In the next tutorial series, we will be looking at how to make the SSTuino recieve inputs from your components, and then have a reaction from that.
Click here to access the next tutorial
Have fun!